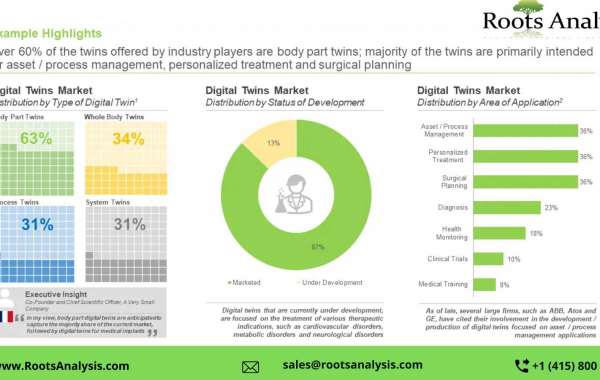
What is Ultrasonic Oxidative Desulfurization?
Ultrasonic oxidative desulfurization combines the power of ultrasound with oxidative chemistry to remove sulfur compounds from biofuels. The process involves the use of ultrasonic waves to create cavitation bubbles in the fuel. These bubbles generate extreme local temperatures and pressures, which break down sulfur-containing molecules. Simultaneously, an oxidizing agent, such as hydrogen peroxide or ozone, is introduced to convert sulfur compounds into sulfoxides or sulfones, which can then be easily separated from the fuel.
Why is UOD a Sustainable Approach?
Energy Efficiency: Unlike conventional methods that require high temperatures and pressures, UOD operates at ambient conditions, significantly reducing energy consumption. The ultrasonic waves enhance the reaction kinetics, making the process faster and more efficient.
Eco-Friendly: UOD minimizes the use of hazardous chemicals and reduces greenhouse gas emissions. The oxidizing agents used are typically environmentally benign, and the process produces fewer byproducts compared to traditional methods.
Versatility: This technique is effective for a wide range of sulfur compounds, including those that are difficult to remove using conventional methods. It can be applied to various biofuels, such as biodiesel and renewable diesel, making it a versatile solution for the industry.
Cost-Effective: By lowering energy requirements and simplifying the separation process, UOD can reduce operational costs. Additionally, the ability to use less expensive oxidizing agents further enhances its economic viability.
Applications in Biofuel Production
UOD is particularly valuable in the production of low-sulfur biofuels, which are essential for meeting stringent environmental regulations. For instance, biodiesel derived from vegetable oils or animal fats often contains trace amounts of sulfur. UOD can effectively reduce these sulfur levels, ensuring compliance with standards such as the Euro VI and EPA Tier 3 regulations.
The Future of UOD
As the demand for cleaner fuels grows, ultrasonic oxidative desulfurization is poised to play a pivotal role in the biofuel industry. Ongoing research aims to optimize the process further, exploring new oxidizing agents and improving ultrasonic reactor designs. With its combination of efficiency, sustainability, and cost-effectiveness, UOD represents a significant step forward in the quest for greener energy solutions.
In conclusion, ultrasonic oxidative desulfurization is a game-changing technology that addresses the challenges of sulfur removal in biofuel production. By embracing this sustainable approach, the biofuel industry can contribute to a cleaner, greener future while meeting the world's energy needs.